What is the TN-S On-Site Electrical System?
A TN-S electrical system is a type of earthing configuration that ensures safety, reliability, and effective fault management by maintaining separate neutral (N) and protective earth (PE) conductors throughout the system. Here’s an in-depth look at what the TN-S system is and why it’s critical for on-site electrical setups.
What is the key characteristic of a TN-S electrical system?
The defining feature of a TN-S system is the what the proper separation of PE and N.
Key considerations for transformer grounding:
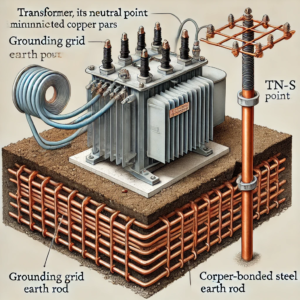
- Ensure the transformer’s neutral point is properly earthed using a grounding grid, earth rod, or other reliable earthing systems. For on-site installations, this grounding must be tested and maintained regularly to ensure low resistance and effective fault current handling.
- Use a reliable grounding grid or earth rod to minimize resistance. For example, a grounding grid made of interconnected copper bars buried in the soil can provide low resistance for fault currents. Alternatively, an earth rod, such as a copper-bonded steel rod driven deep into the ground, can achieve effective grounding in areas with high soil resistivity.
For example, a grounding grid made of interconnected copper bars buried in the soil can provide low resistance for fault currents. Alternatively, an earth rod, such as a copper-bonded steel rod driven deep into the ground, can achieve effective grounding in areas with high soil resistivity.
What makes the TN-S system safe and reliable?
Separation of Neutral (N) and Earth (PE):
This means that the neutral (N) and protective earth (PE) conductors serve distinct purposes and are not interconnected beyond the transformer or Main Earthing Terminal (MET).
- Neutral (N):
- Acts as the return path for electrical current during normal operation.
- Carries current back to the transformer or power source.
- Must be kept isolated from the earth conductor in all downstream wiring.
- Protective Earth (PE):
- Provides a safety path for fault currents to prevent electric shocks.
- Ensures exposed conductive parts (e.g., metal enclosures) are at earth potential.
- Does not carry current under normal operation, only during fault conditions.
By maintaining this separation, the system eliminates parallel paths for current flow, prevents circulating currents, and enhances the detection of faults, ensuring a safe and reliable electrical setup.
This separation eliminates parallel paths for current flow, which prevents circulating currents and ensures that fault currents are safely redirected to the transformer’s grounding point.
Low impedance fault current path:
In the event of a fault, the system provides a direct path to ground through the PE conductor, enabling protective devices to quickly isolate the fault.
What are the key components of a TN-S system?
Protective Earth (PE):
- Dedicated conductor for grounding equipment and protecting against electrical shocks.
Neutral (N):
- Provides a return path for current in normal operation.
Main Earthing Terminal (MET):
- Central point where all PE connections converge.
Circuit Protection:
- Devices like RCDs and MCBs protect the system against faults and overloads.
How does the TN-S system handle fault conditions?
Why is fault handling critical?
Efficient fault management prevents equipment damage, ensures personnel safety, and maintains system reliability.
Fault handling features:
- Low impedance path: Ensures quick fault current flow to the ground.
- Protective devices: Automatically isolate the faulted circuit to prevent hazards.
What are the installation considerations for a TN-S system?
Grounding and Bonding:
- Ensure that all conductive parts are bonded to the PE conductor.
- Avoid creating parallel paths between PE and N to eliminate circulating currents.
Protective Devices:
- Use appropriately rated RCDs, MCBs, and SPDs.
- Ensure device ratings align with the system’s fault current levels.
Cable Sizing:
Properly sizing the phase, neutral, and earth conductors is crucial to ensure the system can handle fault currents and voltage drops effectively.
- Phase Conductors: These must be sized to carry the expected load current under normal operating conditions, with a margin to handle overloads.
- Neutral Conductors: The neutral must be able to carry any imbalance current between phases, especially in three-phase systems, and account for harmonic currents if non-linear loads are present.
- Earth Conductors (PE): Earth conductors should be sized based on the maximum fault current that can flow through them and ensure quick activation of protective devices during faults.
For example, in a 3-phase 400V system, if the load current is 100A, the phase conductors might require a cross-sectional area of 35mm² copper, while the earth conductor might need a minimum of 16mm² to safely handle fault currents. Always follow local electrical codes and standards for accurate sizing.
- Properly size phase, neutral, and earth conductors to handle fault currents and voltage drops effectively.
What are the advantages of a TN-S system?
Safety:
- Minimized risk of electric shock due to efficient fault current management.
Reliability:
- Stable operation with reduced electromagnetic interference.The TN-S system reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) by maintaining the separation of neutral and protective earth conductors. This prevents circulating currents that can generate unwanted electromagnetic fields, which is especially important in environments with sensitive equipment like hospitals, data centers, and industrial facilities. By minimizing EMI, the TN-S system ensures devices operate reliably without disruptions caused by electrical noise.
Compliance:
- Adheres to international standards like IEC 60364 for electrical installations.
Conclusion
A TN-S on-site electrical system is a robust and safe earthing configuration ideal for commercial and industrial facilities. By maintaining the separation of neutral and earth conductors, it ensures efficient fault handling, reduced risks, and compliance with safety standards.
Key Points to Remember:
- Keep neutral and earth conductors separate throughout the system.
- Ensure proper grounding at the transformer and Main Earthing Terminal (MET).
- Remove the PEN jumper to maintain separation of PE and N conductors.
- Use appropriately rated protective devices and conductors.
By understanding and implementing the TN-S system, you can create a safer and more reliable on-site electrical infrastructure.

0 Comments